Upper Nasolabial defect closed with V-Y Nasolabial Cheek Advancement Flap
History:
Patient is a 76 year old female with prior history of non-melanotic skin cancers, lipo-sarcoma, multiple sclerosis and with biopsy proven basal cell carcinoma of the right upper nasolabial crease bordering on the nose and the medial cheek. Patient reports she had noted the lesion for approximately one year before undergoing biopsy by her dermatologist. She denied pain and bleeding from the site.
After resection of the basal cell carcinoma she was referred to Plastic Surgery for repair of the defect.
Findings:
76 year old female with 2.5 x 2.0 cm defect of the right upper nasolabial crease, lateral nose and medial cheek following resection of basal cell carcinoma with 0.5 cm margins. Patient had mobile skin in the cheek and nasolabial regions.
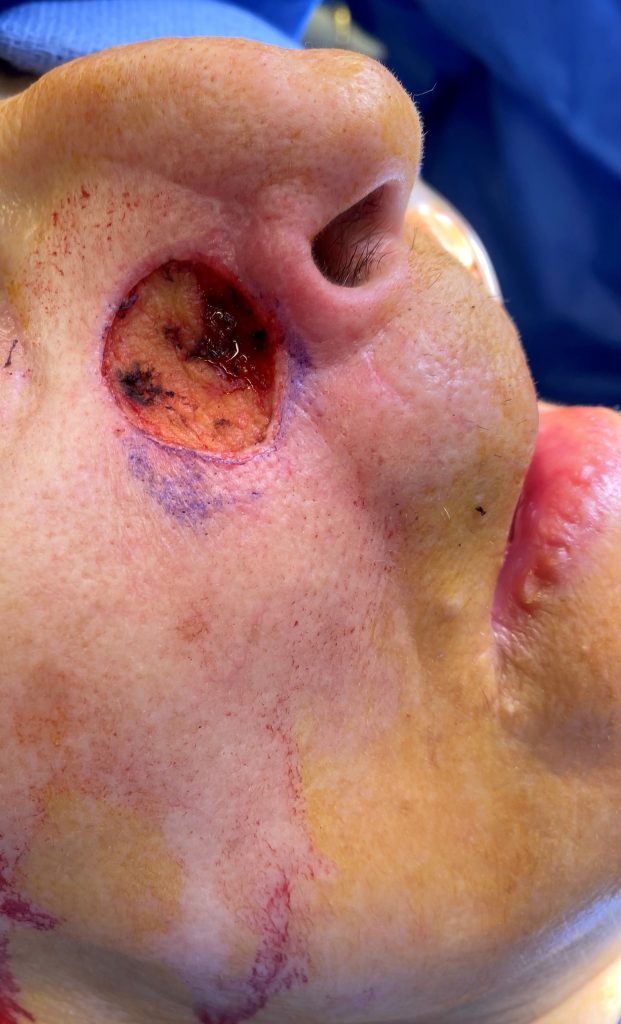
Fig.1: Resultant defect following excision of basal cell carcinoma 2.5 x 2.0 cm
Diagnosis:
Right upper nasolabial skin defect 2.5 x 2.0 cm following excision of basal cell carcinoma
Differential Diagnoses:
Biopsy had shown basal cell carcinoma. Frozen sections confirmed this diagnosis and showed margins free from tumor. It was unlikely that permanent pathological sections would show for instance a basi-squamous carcinoma or a keratoacanthoma.
Workup Required:
No additional work up required. Patient had recently had her yearly physical with routine laboratory tests.
Plan:
After excision of basal cell carcinoma with 0.5 cm margins (Sarcoma surgeon) a reconstruction of right upper nasolabial defect with V-Y nasolabial advancement flap (Plastic surgeon).
Expertise Needed:
Sarcoma surgeon performed excision of basal cell carcinoma with appropriate margins. Plastic surgeon performed local tissue flap reconstruction utilizing knowledge and experience with regional anatomy and aesthetic lines.
Treatment:
Patient underwent excision of right upper nasolabial cheek lesion with 0.5 cm margins by her sarcoma surgeon. This resulted in a 2.5 x 2.0 cm defect of the right upper nasolabial cheek just lateral to the right nasal sidewall, and just superior to the right nasal ala.
Plastic surgery performed the definitive reconstruction with a 2 x 5 cm V-Y nasolabial advancement flap. Design was begun by marking the right nasolabial crease from the inferior aspect of the defect laterally. Next, the entire nasolabial subunit was marked by drawing a line parallel to the nasolabial crease starting from the superior aspect of the defect. This superior line was tapered laterally to meet the marking of the nasolabial crease. Skin was incised with a scalpel along the previously designed markings. Next, needle tip bovie cautery was used to dissect through the tissues. The flap was carefully mobilized by blunt dissection, spreading the underlying soft tissues taking care not to undermine the flap. Once the flap and surrounding tissues were dissected sufficiently to allow mobilization of the flap into the defect, the superomedialaspect of the flap was trimmed to match the medial curvature of the defect. 4-0 monocryl deep dermal sutures were placed, followed by a combination of simple interrupted and running 5-0 prolene sutures. Antibiotic ointment was applied to the incisions.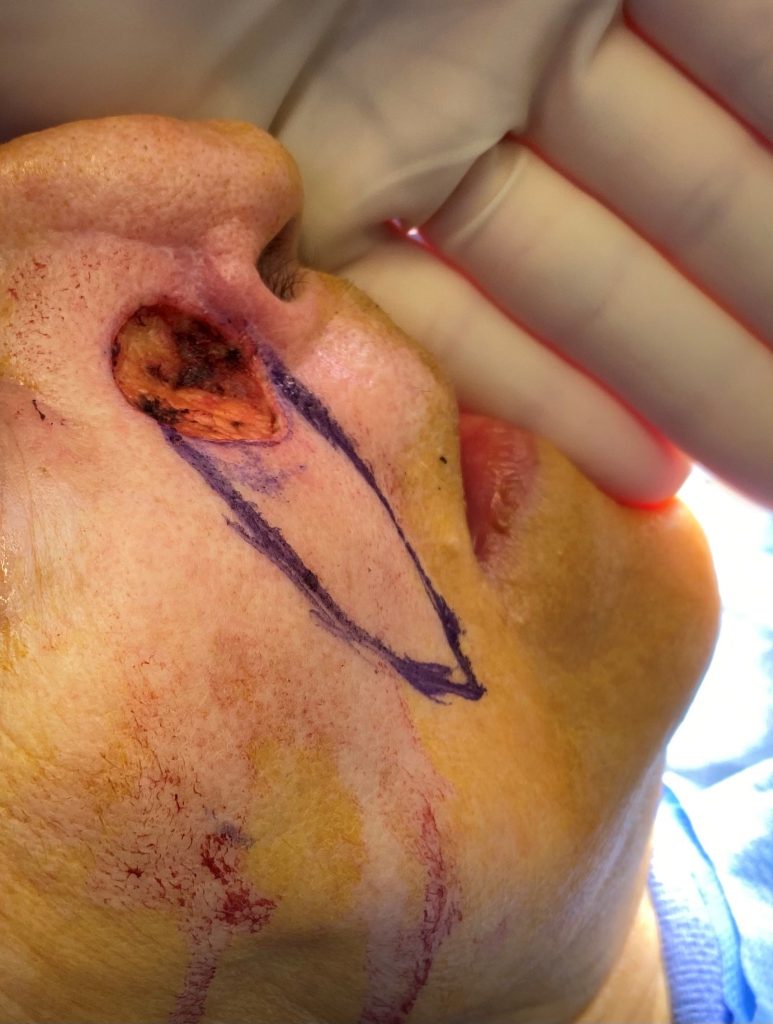
Fig. 2: V-Y nasolabial advancement flap design 2 x 5 cm utilizing entire subunit
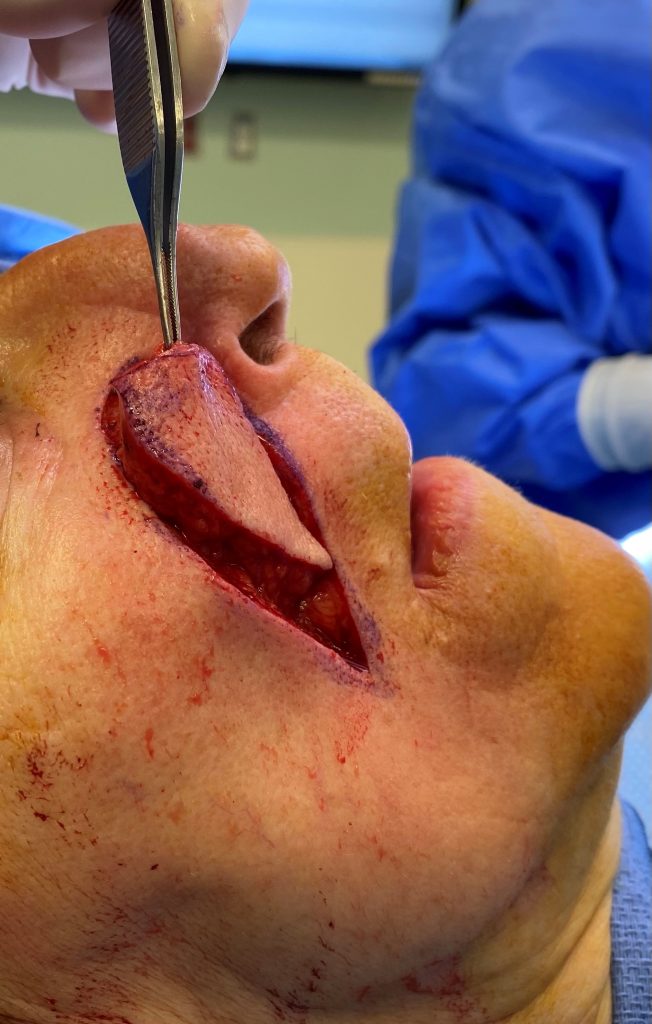
Fig. 3: Mobilization of V-Y flap following dissection
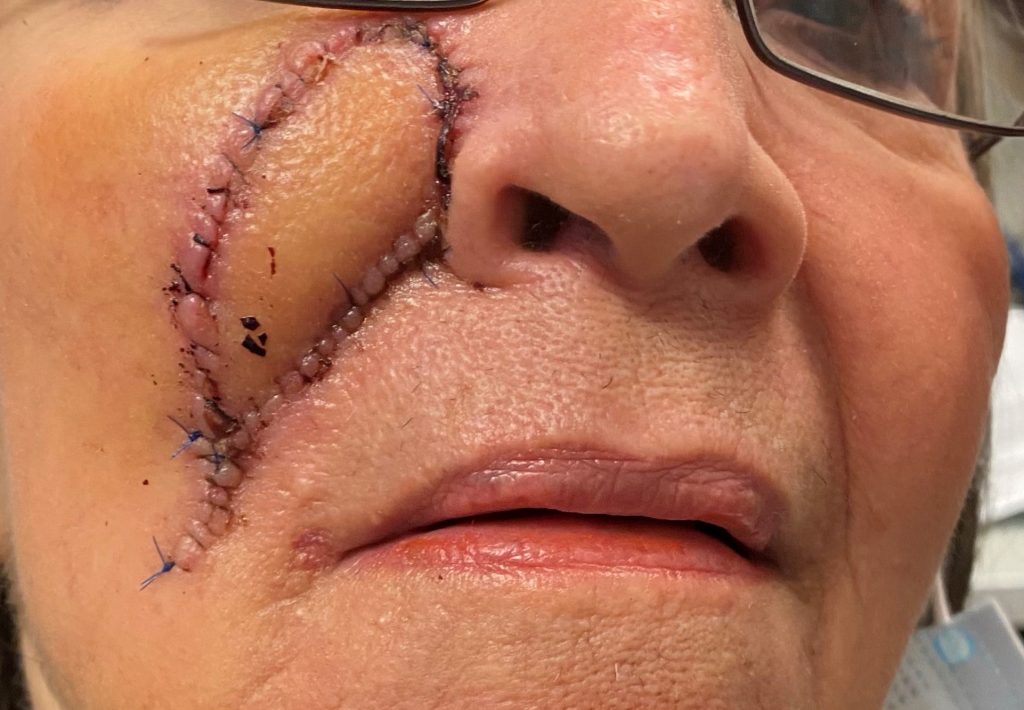
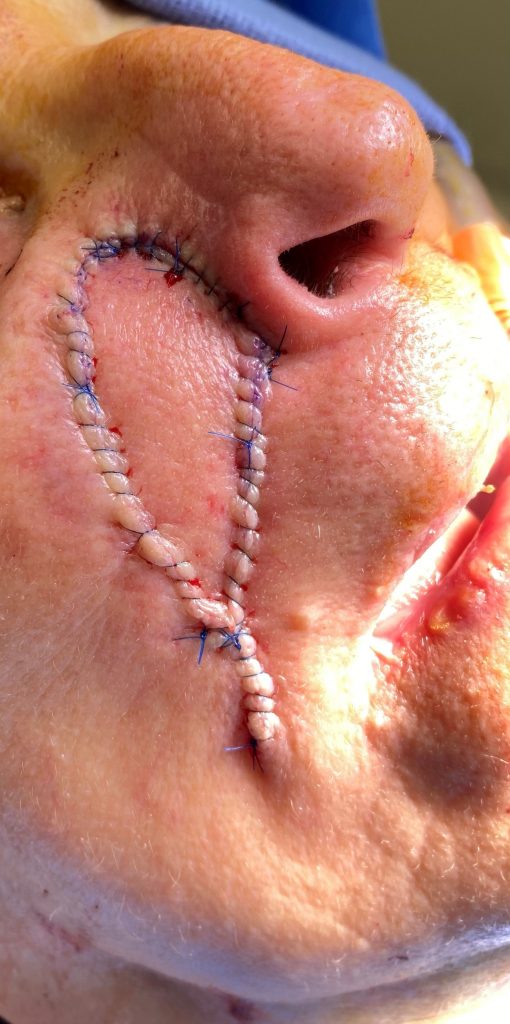
Fig.4; : Post operative inset and advancement of V-Y flap
Follow Up:
Patient was instructed to apply antibiotic ointment to the incisions twice daily for the first two weeks. Sutures were removed post operative day 12. At post operative month 4, patient was noted to have well healed flap with minimal scarring. As the entire aesthetic subunit was raised as a flap, there was no noted distortion of the cheek or lip. Patient was instructed to continue scar massage to soften the underlying scars, and avoidance of direct sunlight to scars.
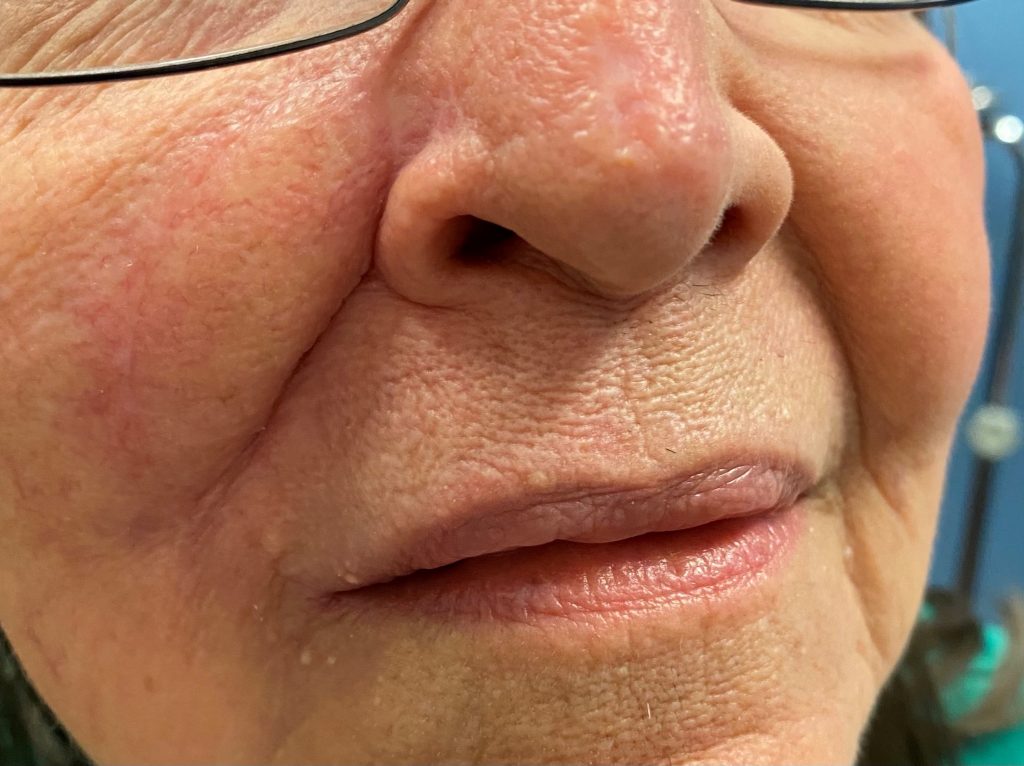
Fig. 6. Preop., intraop. and postop. pictures showed well healed V-Y nasolabial advancement flap 4 months post operative without distortion of cheek or surrounding aesthetic subunits

