Dorsal Hand and Wrist Wounds with Exposed Tendons
History:
56-year-old female struck a deer while riding a motorcycle sustained in addition to a closed head injury, rib, scapular, left femur and transverse spinous process fractures along with an open dorsal wrist and hand wound. Her other life threatening injuries took precedence over her hand wounds.
Findings:

Fig.1. Dorsal Hand & Wrist Wound
Diagnosis:
Differential Diagnoses:
Workup Required:
Plan:
Expertise Needed:
Treatment:
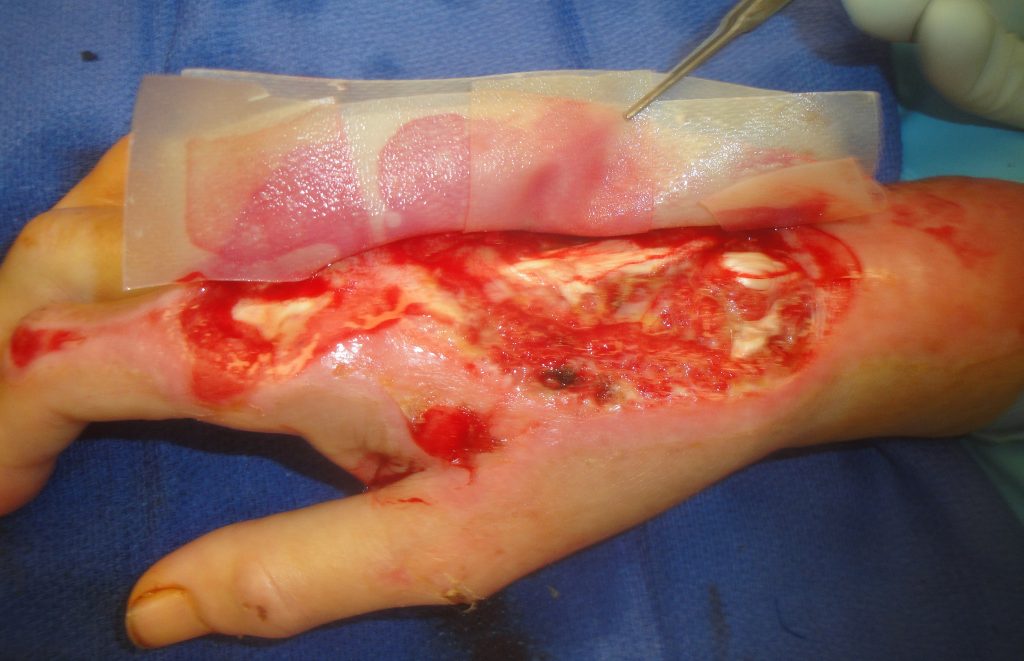
Fig.2. UBM-ECM Wound Device Placement 1
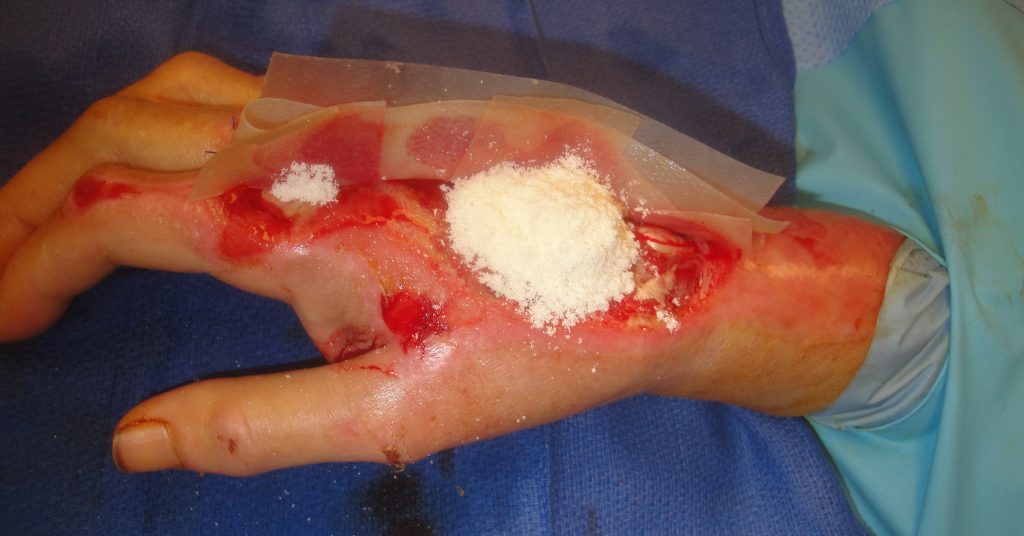
Fig.3. UBM-ECM Wound Device Placement 2

Fig.4. UBM-ECM Wound Device Placement 3

Fig.5. UBM-ECM Wound Device Placement 4
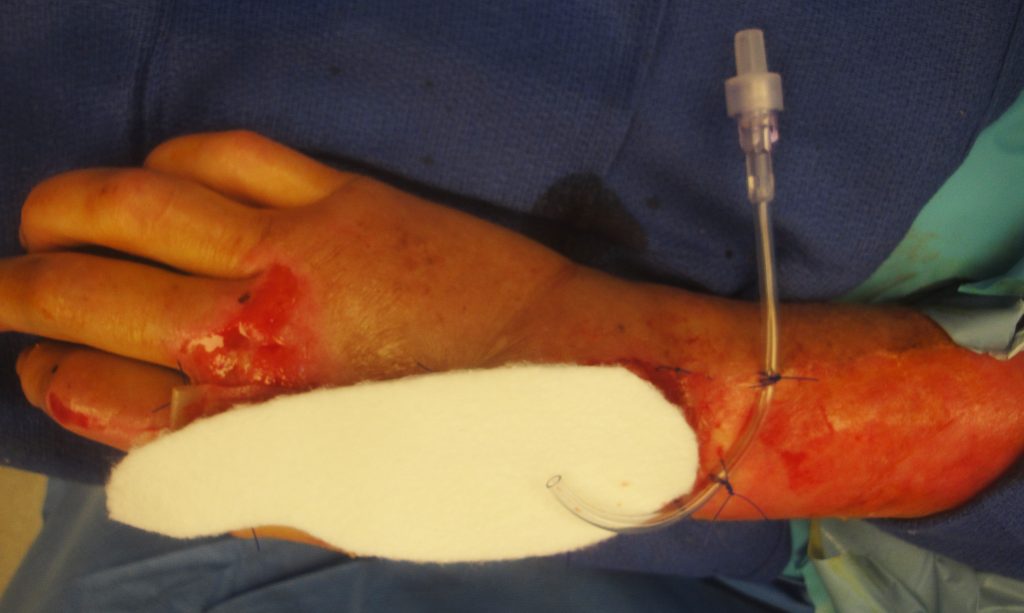
Fig.6. UBM-ECM Wound Device Placement Secondary Dressing

Fig.7. Postoperative wound appearance at week 3
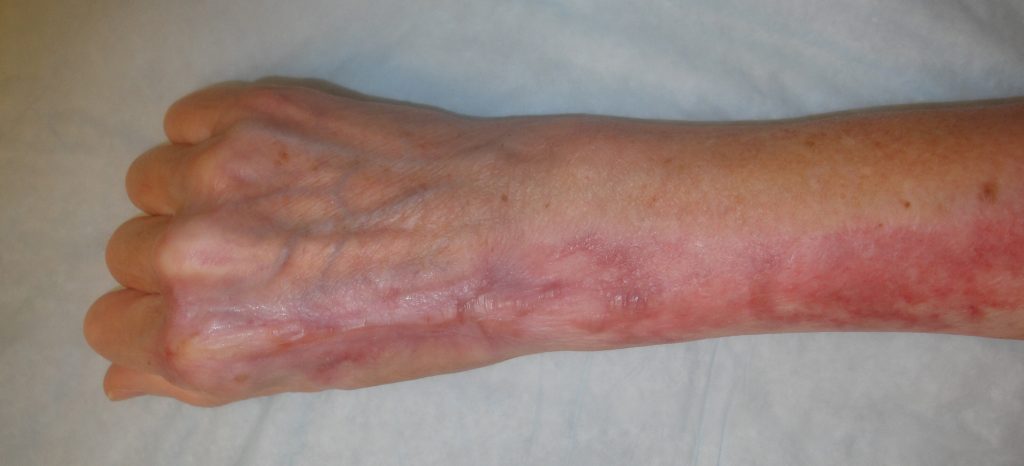
Fig.8. Final wound appearance 8 months post-op.

Final wound appearance 8 months post-op.
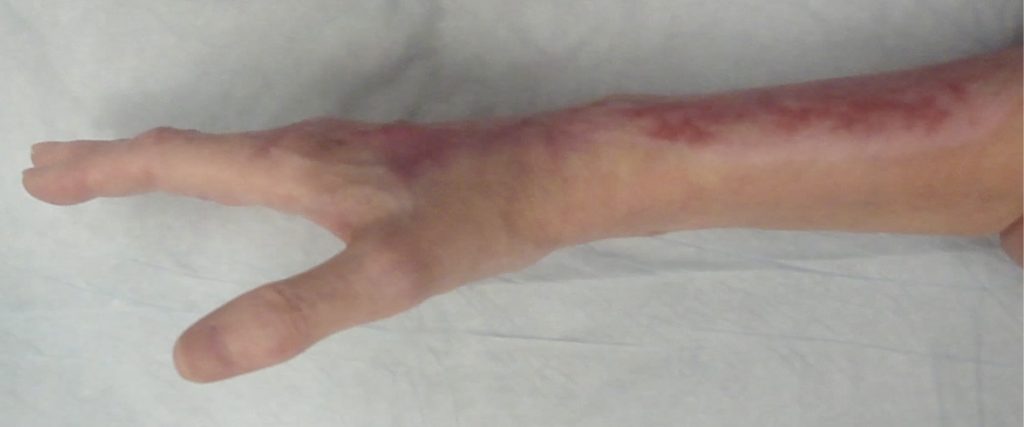
Final wound appearance 8 months post-op.
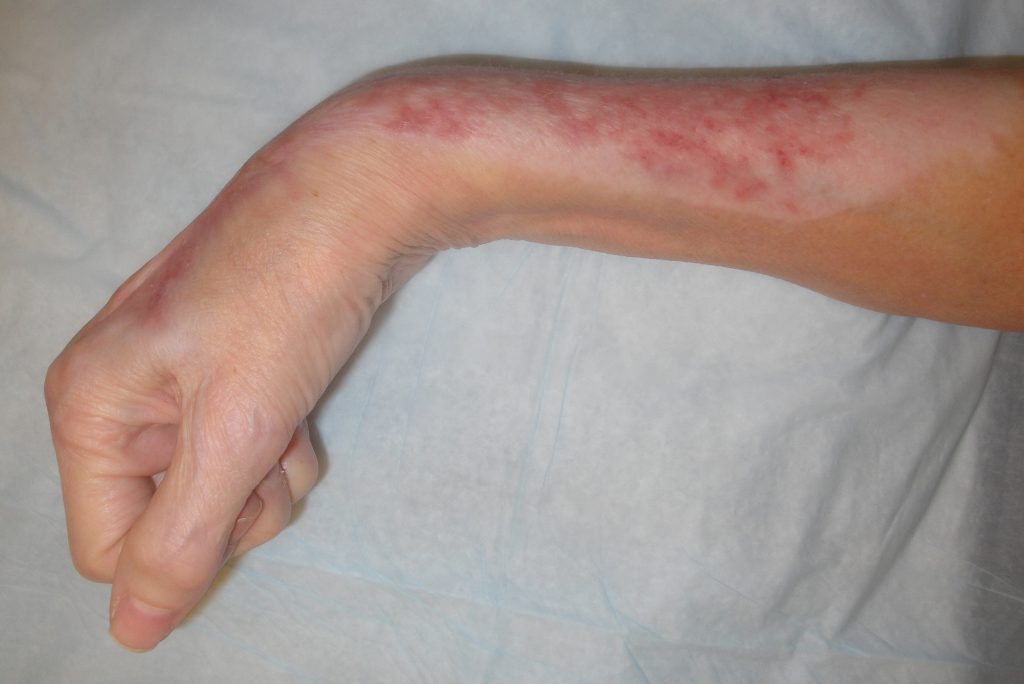
Final wound appearance 8 months post-op.

